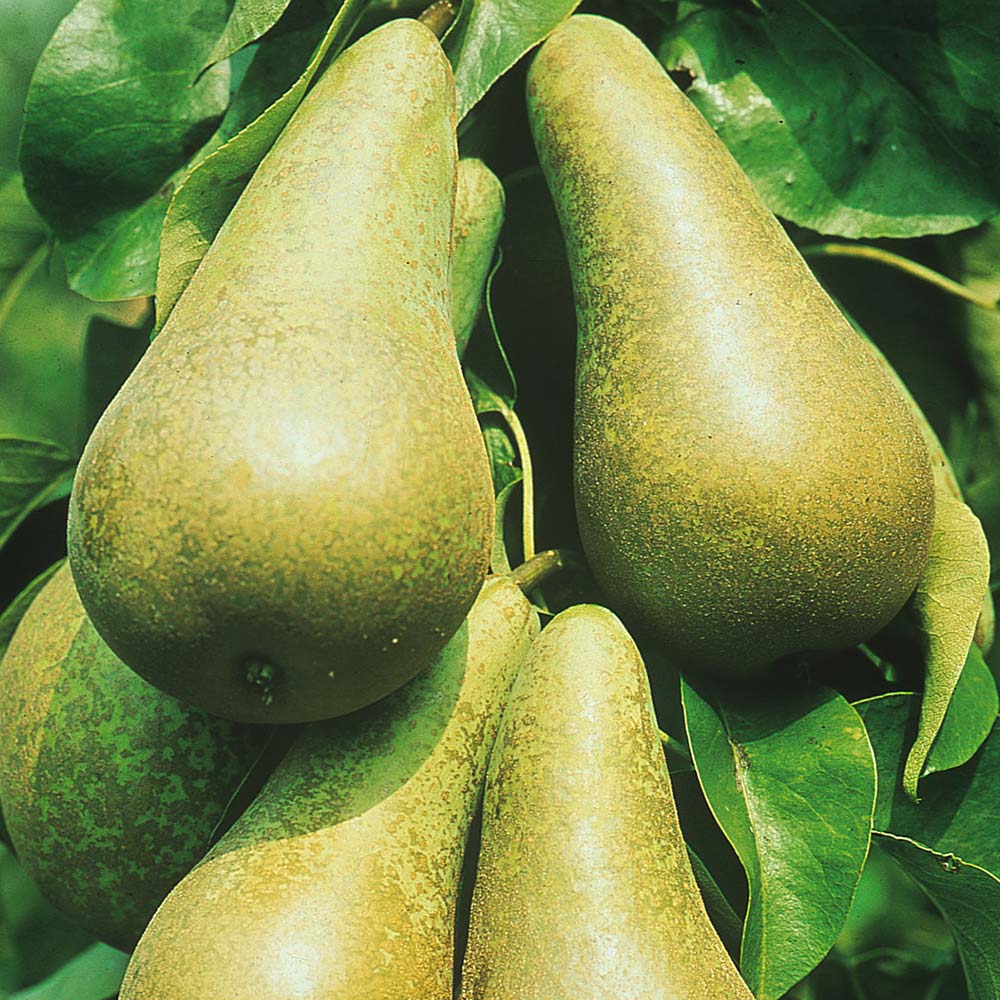
Description
How to grow
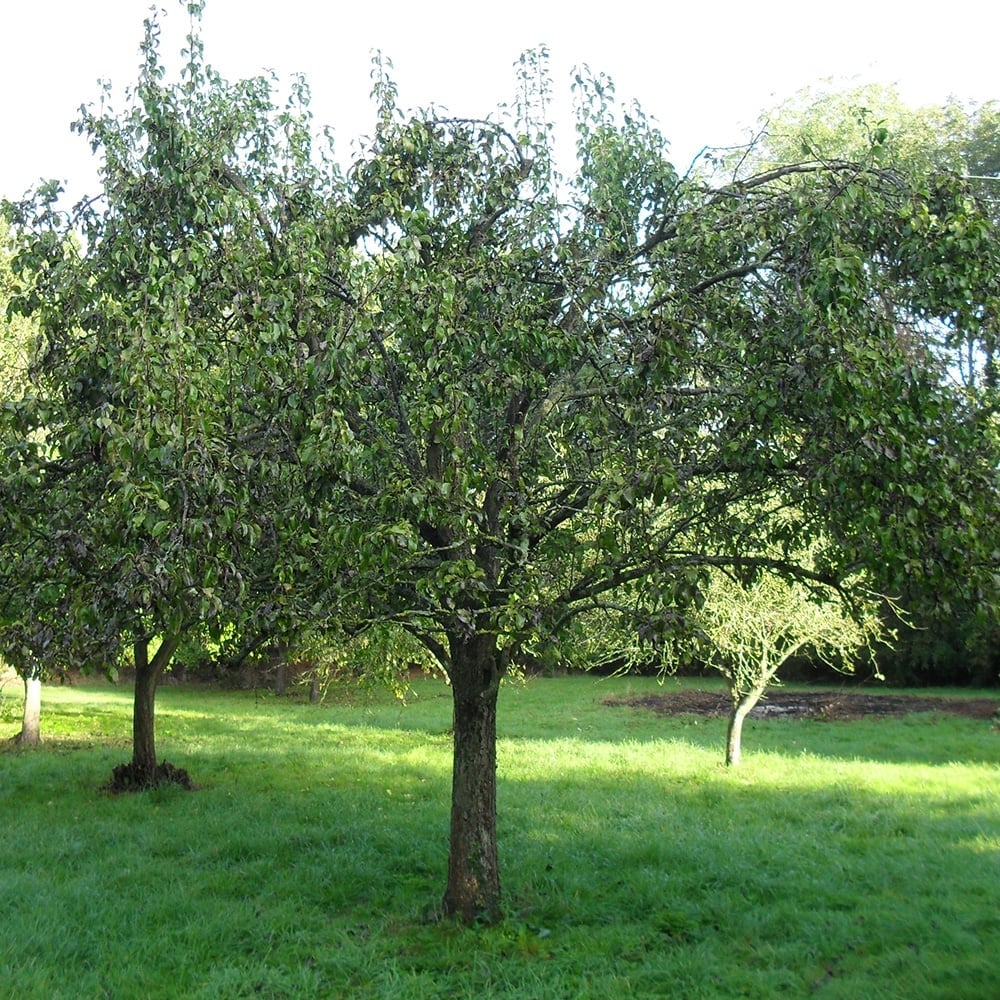
Cultivation Suitable for all training forms. Flowers early and so at risk from spring frosts. Can set fruit without pollination, but tends to fruit better if cross pollinated by another cultivar. Keep a weed free area of 60cm radius around the trunk. Fruit thinning may be needed
Propagation Propagate by grafting or chip budding onto a clonal rootstock for fruit; quince rootstocks are usually used. The rootstock used largely determine the size
Suggested planting locations and garden types Architectural Cottage & Informal Garden
How to care
Pruning Regular pruning required; a spur bearer
Pests May be attacked by aphids, caterpillars, codling moth, bullfinches, pear midge, pear blister mite and pear and cherry slugworm
Diseases No particular resistance or susceptibility. It may be affected by pear rust, brown rot, pear scab, blossom wilt and fireblight.



