Principle species colonised
Mostly Oak, but has been known to affect other Broadleaved trees.
Area affected
Butress and root
Type of decay
Though poorly documented, this process is believed to involve selective delignification, leaving only a mass of white mycelium.
Fruit body / fungal structures
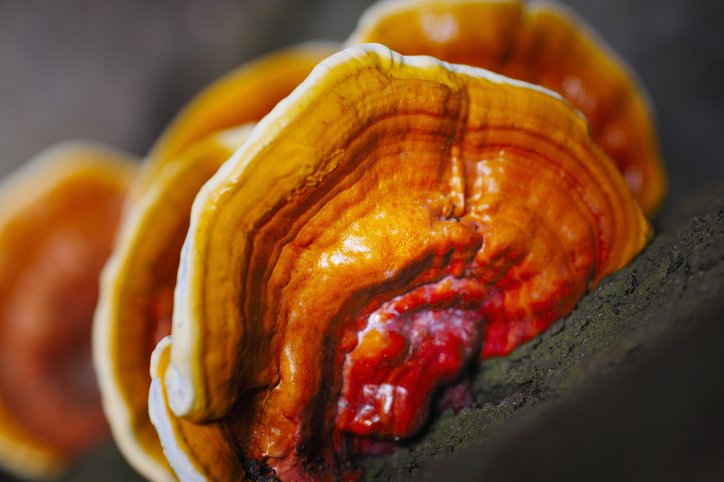
An annual kidney-shaped bracket that is typically carried on a stalk that is originally yellow before turning chestnut and heavily lacquered. The tiny, white pores underneath release brown spores and get discoloured with age. Initially spongy, the texture eventually becomes corky or woody.
Seasonality and perseverance annual, but it may last for a few months before breaking down. The formation season is not well documented.
Significance / Effect / Impact
In the UK, it is quite uncommon on standing trees, although like other Ganoderma species, it can produce white rot, albeit to a limited degree.
Though usually smaller and growing on a stalk, it can be mistaken for G. resinaceum.